Research Project
What are the differences between relative, absolute, and fixed positioning?
17 January 2023
All elements default as block - meaning they take up the who width
of the page. The element's position in the block is default as
static- top, left side of their parent container.
Position: static.
You do not need to define this position as it is the default for
all elements. There are 3 other position values that can allow you
to change the layout of your html page.
- Relative
- Absolute
- Fixed
Relative
This allows you to position your element relative to its default static position. You apply this by adding offset properties - top (moves away from the top, so downwards), bottom (moves away from the bottom, upwards), left (moves away from the left, to the right), right (moves away from the right side, to the left) think opposites. You can specify values in pixels, ems, or percentages.
The element below has a static position.
This is what the element would look like with a relative position with 30px top and 100px left.
Here is the css code for both the static and the relative.

Absolute
When an element’s position is set to absolute, all the other elements on the page will then ignore the element and act like it is not present on the page. It is removed from the normal flow of the document. This may lead to absolute elements overlapping others. The element will then be positioned relative to its closest positioned parent element or and if there isnt one it will base its position on the html tag, which is the top left hand of the page. You then use the same offset properties as relative to determine the final position from there.
This is the static element.
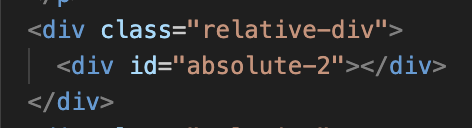
This next element will be relative to the parent div container(which has a position of relative) with 100px right and 25px bottom. The border represents the div.
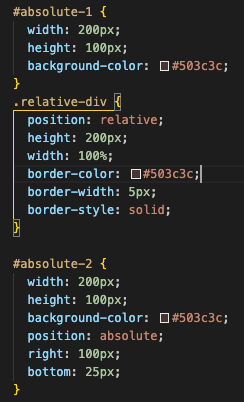
Here is the HTML and CSS code for absolute. You can see the parent element is set to relative.
Fixed
A fixed element does not move from its position even if the page is scrolled. You use the same offset properties and it is relative to the viewport. The signpost image you would have seen on the top right is fixed. It has a offset property of top: 2px and right 50px.
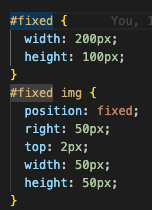
Here is the css code for fixed.
Where I am at
There are so many posibilities with the use of positioning and even though I understand the basic concepts when you start adding in more code and elements the positioning can soon start to have a lot of bugs! I think for me the more I explore and play the more problems and solutions I will learn!
